by Glenda Trinidad, Content Marketing Intern
Artificial intelligence has ignited a new kind of arms race. One that’s not just about computing power, but about energy.
The global “chip war” dominates headlines, but the real competition is happening behind the scenes, in the data centers that power AI. Every new model demands more GPUs, more cooling, and more electricity than the last.
A rack that holds all this infrastructure is roughly the size of a medium fridge, for scale. A single rack aiding the cloud can consume 10 kW of energy; in comparison, racks that are for GPUs use 150-300 kW of energy. That is a lot of energy, but it’s not the most. NVIDIA recently announced an 800 VDC power architecture to support 1 MW rack densities in the future.
This type of power will require a paradigm shift in the way we support this infrastructure from the rack to the site, and even the grid itself.
As AI scales, these invisible demands are reshaping infrastructure, straining local grids, and redefining what efficiency means.
The companies that can balance power, cooling, and performance — turning energy from a constraint into a competitive advantage — will define the next era of computing.
AI “Chip War”
AI is only as powerful as the chip that allows for this high computing power to function. At the heart of this race are GPUs, the engines of machine learning and AI training, capable of processing massive amounts of data at high speed.
The challenge with GPUs is that they consume vast amounts of power, which can generate extreme heat. Many engineers will tell you that creating a low-heat GPU is ideal and part of the ongoing effort to make smart computing better.
That pursuit has now evolved beyond chip design. The real question is no longer just “how powerful can we make GPUs?” but “how efficiently can we power and cool them?”
What will put others above the competition?
The infrastructure of these chips and how efficient they will be in keeping everything cool is a clear player.
Those who solve the economics of power and cooling sustainably will be the true winners of the AI arms race.
Trying to Keep It Cool
Every GPU powering AI workloads releases massive amounts of heat. Controlling that heat is one of the biggest infrastructure challenges in high-performance computing. The difference in temperature can be quite a contrast.
Traditional data centers rely on water-based cooling systems, which can consume thousands of gallons a day. That dependence on local water supplies makes them unsustainable in drought-prone or water-stressed regions.
As AI-optimized compute clusters drive up power density — with rack draws of 60 kW or more, with typical power more around 120-250 kW, and the higher end being 1MW. And site-level energy use is increasing 2 to 10 times that of traditional data centers — cooling has become one of the industry’s greatest challenges. Water-based systems risk straining local supplies, especially in drought-prone regions, making them increasingly unsustainable in the long run.
To solve this, new methods like air and liquid cooling are transforming data-center design. These innovations drastically reduce water use while maintaining performance, which is a crucial balance as global computing demand soars.
But keeping things cool is only part of the equation.
Waste To Energy
Every watt of power that goes into AI eventually becomes heat. Instead of releasing it into the atmosphere, forward-thinking operators are finding ways to capture and reuse it.
District-heating systems can capture and redirect excess heat to warm nearby buildings, while industrial facilities can reuse it as a low-cost energy input. Sensors and automation enable data centers to detect, manage, and distribute that heat efficiently.
This circular approach doesn’t just reduce waste, it redefines efficiency. Companies that treat heat as a resource, not a byproduct, are building the next generation of sustainable AI infrastructure.
Already, there are companies such as Provacative Earth that are working on this by using carbon capture filters that capture this type of excess heat.
AI Clustering
AI’s progress depends on scale. Each new generation of models requires larger compute clusters — massive networks of GPUs working together to train and process data at unprecedented speeds.
These clusters can be ten to thirty times more energy-dense than traditional data centers, putting new pressure on local grids and cooling systems alike. They can also cycle 98% of their power in just milliseconds, talk about powerful!
To put this in perspective, imagine a 1GW data center; it can go from full power to 200kW in 1 millisecond and then power back to full. This can cause issues for the grid, which is why supporting the infrastructure is vital.
This shift is reshaping how data centers are built. Efficiency can no longer be measured only in compute performance; it must account for power, cooling, and sustainability together.
In short, the next frontier of AI isn’t just about smarter algorithms. It’s about smarter energy.
The leaders who master both will set the pace for an industry where efficiency is the ultimate measure of intelligence.
The Soluna Model
AI’s energy problem can’t be solved with yesterday’s infrastructure.
It demands a new model. One built from the ground up to align computing with clean, abundant power.
At Soluna, we’re designing exactly that.
Our behind-the-meter data centers connect directly to renewable sources like wind and solar, using power that would otherwise be wasted through curtailment. By converting that stranded energy into productive computing capacity, we create value for both the grid and the future of AI.
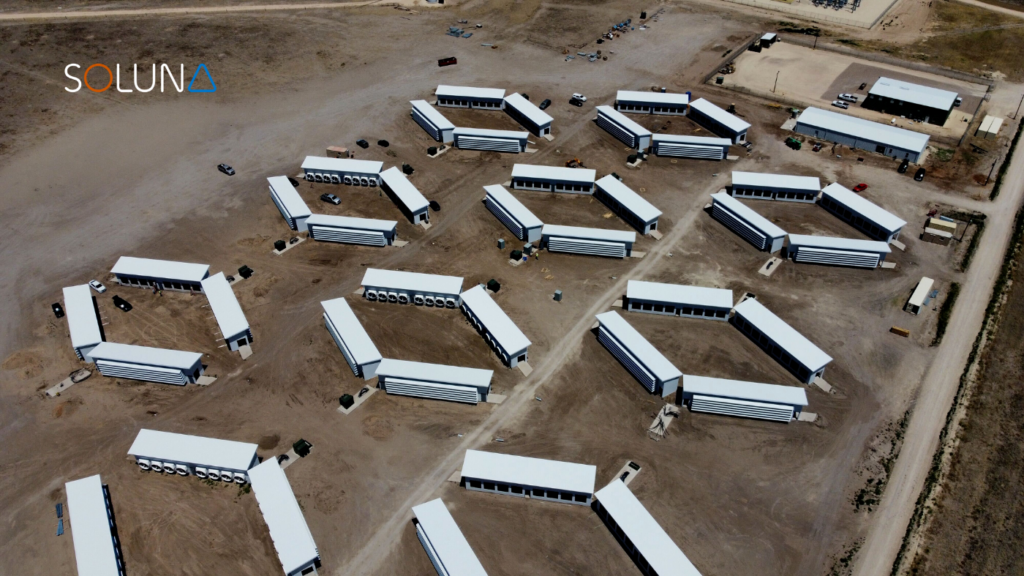
Each facility is engineered for efficiency and adaptability. Our air-first cooling systems minimize water use while maintaining high performance, and our modular architecture allows us to scale capacity quickly and responsibly, wherever renewable energy is available.
Unlike conventional data centers built around real estate or network proximity, Soluna builds around energy itself. We bring compute to the power source, not the other way around — creating a model that is more sustainable, more flexible, and more resilient to grid constraints.
The future of AI infrastructure will be defined by those who can make computing clean, efficient, and scalable. That’s the future Soluna is already building.
Who Will Win the AI Arms Race?
AI is reshaping every industry. Its future will be determined not by algorithms alone, but by the infrastructure that sustains them.
The winners of this new arms race won’t simply train the largest models; they’ll build the smartest systems — those that align performance with sustainability, innovation with responsibility.
At Soluna, we’re proving that the two can coexist. By pairing high-performance computing with renewable power, we’re redefining what progress looks like in the AI era. The next great leap in intelligence won’t come from more code. It will come from how we power it.
Learn more about Soluna visit → https://www.solunacomputing.com/